The LEO R&D Strategy, Part 1: National Diplomatic Spacepower
Business in Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) is booming. What is the United States going to do about this? Wonder no longer.

Business in Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) is booming. We appear to be on the cusp of substantially increased commercial and human spaceflight. What is the United States going to do about this? Wonder no longer. Very recently the United States National Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Research & Development (R&D) Strategy was released by the National Science and Technology Council. Let's dig into this document and try to understand some of its efforts, expected outcomes, and implications.
The Untied States National Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Research and Development (R&D) Strategy takes an open-handed, transparent, and mutually beneficial approach to research and development in LEO. "Commercial LEO destinations" with international partnerships, leadership in responsible and sustainable norms of behavior, standards for human spaceflight safety, and freely and publicly available research and data are foundational efforts for this strategy. The objectives, efforts, and expected outcomes will further strengthen United States soft diplomatic spacepower and benefit the international community.
This article echoes a previous essay diplomatic spacepower analysis on the National Cislunar Science & Technology Policy. In our quest to digest what the National LEO R&D Strategy means for diplomatic spacepower, we will 1) review what national and diplomatic spacepower are, 2) identify what the new strategy is planning, and 3) attempt to understand how these activities will improve United States diplomatic spacepower.
Skol!
1) What is National Spacepower?
I've posted a short primer on national spacepower for the interested reader. The TL;DR is:
"National spacepower is the sum of all resources and capabilities a nation possesses to influence and control events, outcomes, and other actors in the Space Domain in pursuit of prosperity and security." (What is Spacepower and Why You Should Care!)
As you may imagine, national spacepower is sometimes decomposed into a number of aspects to assist problem-solving and planning. A common framework is DIME, standing for Diplomatic, Informational, Military, and Economic (pg. I-12, 13, U.S. DoD Joint Publication 1 (JP-1)).
Using the DIME framework, planners and strategists can consider how to build a strategy to achieve a specific outcome with regards to national prosperity and security.
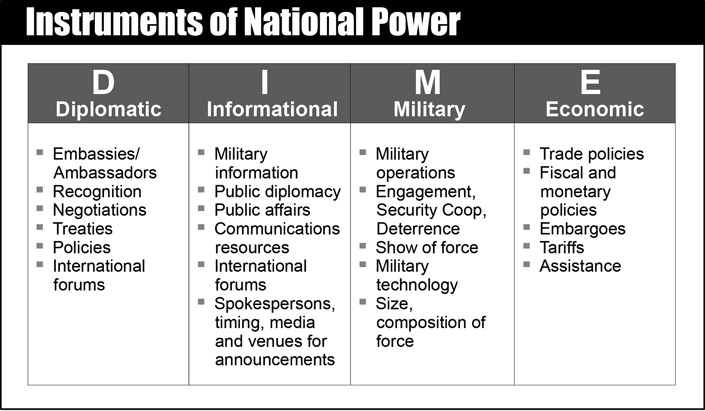
Here, we're going to use a Diplomatic (and in another article, Economic) lens to understand how United States national spacepower is being built using the LEO R&D Strategy.
2) Diplomatic Spacepower Elements of the Strategy
The strategy proposes 5 principal objectives:
"1. Advance groundbreaking science & technology [...].
2. Strengthen U.S. Government collaboration and partnerships [...].
3. Promote market opportunities, innovation, and sustainability [...].
4. Expand international cooperation [...].
5. Stimulate science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education and workforce development [...]."
(pg. 5, National LEO R&D Strategy)
In this essay we are concerned with how the United States will achieve these objectives - specifically with respect to how National Diplomatic Power is strengthened.

I am breaking these into individual supporting endeavors identified within the strategy in the following subsections.
Scientific Research in Space
A strong theme found throughout the document is cleaving to the principles identified in the 1969 Outer Space Treaty:
"[T]he U.S. Government will continue to support the exploration and use of space for peaceful purposes, including the use of LEO for R&D." (pg. 10, National LEO R&D Strategy)
As part of this, the strategy also endeavors to collaborate with international partners, intending to:
"[Remain] the global leader and partner of choice for orbital platforms and other space research facilities." (pg. 14, National LEO R&D Strategy)
Along this vein, the strategy goes on to say:
"Future technological progress in space will be propelled by the U.S. Government empowering the free market, while working with allies and partners to protect IP." (pg. 11, National LEO R&D Strategy)
In essence, the strategy proposes substantive international collaboration with 'allies and international partners' in pursuit of propagating the cooperative use of space for peaceful purposes.
Another thrust related to research revolves around academic research. In particular:
"[T]he U.S. Government will explore establishing collaborative frameworks, such as institutes and consortia, which would be responsible for enabling engagement and collaboration across government, academia, industry, and international partners." (pg. 9, National LEO R&D Strategy)
and
"The U.S. Government will also continue to encourage transparency, data sharing, interoperability, and related norms that facilitate international cooperation in space-based fundamental research." (pg. 12, National LEO R&D Strategy)
Not only will international teams be funded to conduct research, but their publications and data will be 'freely and publicly accessible' to the world:
"The 2022 OSTP Public Access Memorandum outlines expectations for Federal departments and agencies to increase free, immediate, and equitable access to federally funded research, building on U.S. efforts to advance policy that benefits all of America." (pg. 9, National LEO R&D Strategy)

The strategy goes on to add:
"The U.S. Government supports making scientific data underlying peer-reviewed scholarly publications resulting from federally-funded research freely available and publicly accessible by default at the time of publication, unless subject to limitations, such as legal, privacy, ethical, technical, intellectual property (IP), or security limitations." (pg. 9, National LEO R&D Strategy)
Public accessibility (with guardrails) of papers and data is not the current norm in academic literature. This will require a change in the publishing industry business model and, likely, university or federal hosting services for data. These changes will cause heartburn with publishers and academic researchers over the coming years.

However, free and open access to papers and underlying data will 1) meaningfully improve research and education, particularly at international institutions that cannot afford publisher subscriptions, and 2) improve national and international reproducibility of published results.
Freely and publicly available access to papers and data demonstrate substantial openness and transparency in research beyond today's norms.
Space Sustainability & Norms of Responsible Behavior
The sustainability of the space domain for future use is threatened by buildup of space debris, particularly in LEO. This long-recognized problem is addressed in several passages of the LEO R&D strategy.
First, an affirmation that the United States will continue to champion responsible norms of behavior is made.
"Using the entrepreneurial nature, creativity, and innovative capabilities of commercial enterprise, coupled with diplomatic engagements, the United States will conduct regular outreach to international stakeholders, comply with our international obligations, and champion norms of responsible behaviors in LEO." (pg. 12, National LEO R&D Strategy)
Additional statements related to maintaining the spirit and intent of the Outer Space Treaty are also mentioned.
Orbital debris mitigation strategies are also proposed:
"[T]he U.S. Government promotes best practices, guidelines, and other rules of the road, as well as technological improvements that enable the enduring use of the LEO ecosystem. The U.S. Government will continue scientific and technological research and development to prevent and address orbital debris as well as to develop novel technologies to increase spacecraft endurance." (pg. 10, National LEO R&D Strategy)
So, not only is orbital debris mitigation R&D proposed, but hardening of spacecraft to small / fine orbital debris is also discussed.
Human Spaceflight Safety
Substantially increased human presence in space - both national and commercial - are expected. In particular:
"Following the [2030] retirement of the ISS, the U.S. Government will rely on commercial space stations for crewed and autonomous on-orbit research." (pg. 6, National LEO R&D Strategy)
Expanding further upon this,
"These LEO platforms, called “commercial LEO destinations,” will be privately-owned and operated facilities in space with the capacity for conducting research." (pg. 6, National LEO R&D Strategy)
An increased human presence in LEO has implications that dovetail with space sustainability. Because space debris and poor norms of behavior place human lives at risk, human spaceflight safety is also a strategic thrust for the United States.
"[T]he United States will lead in the development and implementation of open, transparent, and credible international policies and practices for human spaceflight safety." (pg. 12, National LEO R&D Strategy)
and
"The United States will promote the use of common, internationally recognized standards when sharing orbital information on human spaceflight missions and potential hazards to the life or health of astronauts." (pg. 12, National LEO R&D Strategy)
Openness and transparency in human spaceflight is a necessary component of human spaceflight safety when multiple spacefaring nations have simultaneous projects and competing national interests in space.
The connections to Civil Space Traffic Management (Civil STM) and Space Situational Awareness (SSA) are straightforward:
"Working closely with industry partners, international organizations, and other government agencies to develop innovative solutions that can enhance SSA, reduce operational risks, and enable faster emergency response;" (pg. 13, National LEO R&D Strategy)"
We may grin when we say it, but how far away are we from a LEO equivalent to the Coast Guard?
Let's turn our attention to how these proposed efforts affect United States diplomatic spacepower.
3) What Does This Mean for Diplomatic Spacepower?
All of these efforts bolster soft diplomatic power; they are likely to align interests of the international community to minimize conflict, support transparency, and encourage joint space-focused enterprises.
Human spaceflight safety is expected to be much more commercial than seen in previous years. In the entrepreneurial pursuit of profit "commercial LEO destinations" will likely involve a wide variety of on-orbit international employees and participants. A wider family of nations will have every incentive to participate in LEO commercial activities, deeply aligning international interests in LEO with the United States.
In turn, this reinforces the continued establishment and progress in responsible norms of behavior in space. Crewed commercial LEO destinations, infrastructure, and increased international commercial activity in space provide powerful motivation for codification of space sustainability initiatives.
Similarly, human spaceflight - also at risk from reckless commercial or state behavior and orbital debris - will benefit from establishment of open and transparent data sharing and communication of intentions in LEO.
Perhaps an International Civil STM or SSA infrastructure prototype is on the horizon.

Finally, given the massive federal R&D funding provided by the United States Government, it is encouraging to see a renewed commitment to integrating international researchers into proposed LEO R&D projects. In a fit of foot-stomping, I'll also emphasize that the global benefits of requiring free access to publications and underlying data will have medium- and long-term benefits to the international community.
The open-handed, transparent, and mutually beneficial approach proposed in this LEO R&D strategy goes a long way towards aligning international interests and incentivizing responsible (and profitable!) behavior in space.
I believe that all of these objectives, efforts, and expected outcomes will further strengthen United States soft diplomatic spacepower.
Summary
The National LEO R&D Strategy identifies 5 objectives. Several concrete efforts are proposed to achieve these desired outcomes, many of which support and improve United States Diplomatic Spacepower. Specifically:
- "Commercial LEO destinations" with international partnerships will replace the International Space Station. International entrepreneurial projects in space will more tightly connect the international community.
- Leadership in responsible and sustainable norms of behavior will continue, ensuring that growing space commercial and infrastructure can continue to serve the international community and that international consensus on space sustainability is achieved.
- Standards for human spaceflight safety will be established. These will integrate tightly with international commercial endeavors and consensus on sustainable and safe norms of behavior in LEO.
- Freely and publicly available research and underlying data will improve the quality and accessibility of international LEO R&D. Developing nations, education institutions, and research laboratories will have a lower barrier of entry to contribute meaningfully to humanity's knowledge.
Subscribe to the Newsletter
If you enjoy this content, show your support by subscribing to the free weekly newsletter, which includes the weekly articles as well as additional comments from me. There are great reasons to do so, and subscriptions give me motivation to continue writing these articles! Subscribe today!


